Social networking refers to the use of internet-based platforms that enable individuals and organizations to interact, share information, and engage in community-based activities. These platforms facilitate the creation of social networks by connecting users with friends, colleagues, and others who share similar interests or connections.
The history of social networking platforms can be traced back to the late 1990s and early 2000s. The earliest forms of social networking were online communities such as SixDegrees.com, which launched in 1997. This was followed by the advent of platforms like Friendster in 2002 and MySpace in 2003, which further popularized the concept of online social networks. However, it was the launch of Facebook in 2004 that marked a significant turning point, as it introduced features that revolutionized the way people connect and interact online. Other platforms like Twitter (2006), Instagram (2010), and Snapchat (2011) later emerged, each offering unique ways of interaction and sharing content.
In the current digital era, social networking platforms have become integral to the global communication landscape. They offer unprecedented opportunities for personal and professional networking, brand marketing, social activism, and cross-cultural interaction. With billions of users worldwide, these platforms have a significant impact on social dynamics, influencing everything from how news is disseminated to how businesses interact with their customers. Their global reach extends across borders, making them powerful tools for connecting people from different parts of the world, fostering international collaboration and understanding.
Table of Contents
The Evolution of Social Networking
The evolution of social networking has been marked by significant shifts in how people connect and communicate online. This evolution can be understood through the lens of various key platforms that have emerged over the years.
- Early Platforms like Friendster and MySpace: The early 2000s saw the rise of platforms like Friendster (2002) and MySpace (2003). Friendster was one of the first to use a network of friends to build connections, while MySpace allowed users to customize their profile pages and became a popular platform for musicians to share their work. These sites laid the foundation for modern social networking by emphasizing user-profiles and the concept of connecting with friends online.
The Rise of Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn:
- Facebook, launched in 2004, quickly eclipsed its predecessors due to its user-friendly interface and constantly evolving features. It became the standard for social networking, allowing people to connect with friends, share photos and videos, and join groups of like-minded individuals.
- Twitter, introduced in 2006, brought a different flavor to the social media landscape with its microblogging format that limits posts to 280 characters, making it popular for real-time updates, news sharing, and public discourse.
- Instagram, started in 2010, revolutionized photo sharing with its focus on visual content and later, short-form videos. It became a platform for influencers, brands, and everyday users to share visually appealing content.
- LinkedIn, more focused on professional networking, emerged as the go-to platform for career-related connections, job searches, and professional content sharing.
Emergence of Newer Platforms like TikTok and Clubhouse:
- TikTok, launched internationally in 2017, brought a new dimension to social networking with its short-form, video-focused content. It quickly gained immense popularity, particularly among younger audiences, for its engaging, creative, and often viral content.
- Clubhouse, released in 2020, introduced an audio-chat-based social networking platform. It distinguished itself by hosting live, audio-only discussions, allowing users to join “rooms” to listen or participate in conversations on various topics.
Each of these platforms has contributed to the dynamic landscape of social networking, offering unique ways for people to connect, share, and consume content. This evolution reflects changing user preferences and technological advancements, indicating that social networking will continue to adapt and grow in the future.
Impact on Society
Social networking has had a profound impact on society, particularly in the way we communicate, connect globally, and its varied influence on different age groups and communities.
Changing Communication Patterns:
- Instant and Diverse Communication: Social networking has revolutionized communication, making it instant and accessible. Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and WhatsApp enable real-time sharing of thoughts, images, and videos, transcending traditional barriers like distance and time.
- Visual and Multimedia Communication: The rise of Instagram and TikTok highlights a shift towards more visual and multimedia forms of communication. People increasingly use images, videos, and memes to express themselves, which can often convey emotions and ideas more effectively than text.
- Public vs. Private Communication: Social media blurs the lines between public and private communication. While it allows for personal expression in a public forum, it also raises concerns about privacy and the permanence of online interactions.
Fostering Global Connections:
- Breaking Down Geographical Barriers: Social networking sites have played a crucial role in connecting people across different geographical locations, fostering cross-cultural exchanges and understanding.
- Creating Online Communities: They enable the formation of global online communities based on shared interests or causes, regardless of physical location. This has been particularly significant for marginalized groups or those with niche interests.
- International Collaboration and Awareness: Platforms like LinkedIn facilitate professional networking across borders, while Twitter and Facebook can raise awareness and mobilize support for global issues like climate change or human rights.
Impact on Different Age Groups and Communities:
- Youth and Digital Natives: Younger generations, who are digital natives, are particularly influenced by social networking. It shapes their social interactions, information consumption, and even their sense of identity. However, there are concerns about the impact on mental health, cyberbullying, and the pressure of online personas.
- Older Generations: For older generations, social networking can be a tool for staying connected with family and friends, especially those who are geographically distant. It also offers avenues for lifelong learning and engagement with broader communities.
- Impact on Diverse Communities: Social media has given a voice to diverse communities, allowing for greater representation and advocacy. However, it also poses challenges, such as the spread of misinformation and the digital divide, which can exclude those without access to technology.
Overall, the impact of social networking on society is multifaceted, offering numerous benefits in terms of connectivity and communication, while also presenting challenges that need to be addressed to ensure a positive and inclusive digital environment.
Economic Impact
The economic impact of social media is vast and multifaceted, significantly influencing marketing strategies, consumer behavior, and giving rise to the influencer culture, each with substantial economic implications.
Social Media as a Tool for Marketing and Business:
- Marketing and Advertising: Social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter have become crucial channels for digital marketing. Businesses, from startups to large corporations, use these platforms to advertise products, engage with customers, and build brand awareness. The ability to target ads based on user data has made social media advertising highly effective.
- Customer Engagement and Feedback: Social media allows businesses to engage directly with customers, providing a platform for customer service, feedback, and community building. This direct interaction can enhance customer loyalty and improve brand reputation.
- E-Commerce Integration: Platforms like Instagram and Facebook have integrated e-commerce features, allowing users to purchase products directly through the app. This seamless integration has further blurred the lines between social networking and online shopping.
Influence on Consumer Behavior:
- Shaping Buying Decisions: Social media significantly influences consumer behavior. Reviews, testimonials, and user-generated content on these platforms can sway buying decisions. The phenomenon of “social proof,” where people’s choices are influenced by the actions of others, is prevalent.
- Trendsetting and Viral Products: Social media has the power to quickly popularize products and trends. Items that go viral on platforms like TikTok can see a sudden surge in demand, exemplifying the platform’s impact on consumer choices.
The Rise of Influencer Culture and Its Economic Implications:
- Influencer Marketing: The rise of influencers – social media personalities with large followings – has created a new paradigm in marketing. Brands collaborate with influencers to promote products, tapping into the influencer’s credibility and reach. This has become a lucrative industry, with top influencers commanding substantial fees for their endorsements.
- Micro-Influencers and Niche Marketing: Beyond celebrities, micro-influencers with smaller but highly engaged followings are increasingly sought after for more targeted marketing campaigns. They often hold sway in specific niches, providing access to specific demographic groups.
- Economic Opportunities and Challenges: Influencer marketing has opened new economic opportunities, not only for influencers but also for agencies and platforms that facilitate these partnerships. However, this trend also brings challenges, such as the need for transparency, issues of authenticity, and the potential for misleading advertising.
Social media’s economic impact is profound, reshaping marketing strategies, influencing consumer behavior, and giving rise to a new economic sector centered around influencer culture. As social media continues to evolve, its economic implications are likely to expand and diversify further.
Cultural Influence
Social media’s cultural influence is immense, playing a pivotal role in shaping modern culture, spreading trends and information, and impacting language and communication styles.
Shaping Modern Culture:
- Global Cultural Exchange: Social media platforms enable a rapid exchange of cultural ideas, practices, and expressions across borders. This has facilitated a more globalized culture where trends, music, art, and even political ideas can gain international attention quickly.
- Redefining Entertainment and Media: The rise of platforms like YouTube, TikTok, and Instagram has changed the landscape of entertainment. These platforms allow users to not only consume content but also create and share their own, leading to a democratization of content creation.
- Social Movements and Awareness: Social media has become a crucial tool for organizing and promoting social movements and activism, from #MeToo to Black Lives Matter. It amplifies voices and aids in mobilizing support for various causes, impacting societal norms and values.
Spread of Trends and Information:
- Viral Trends and Memes: Social media is a breeding ground for viral trends and memes. These can range from fashion and lifestyle trends to humorous or satirical content, influencing various aspects of culture and daily life.
- News and Information Dissemination: Social media has become a primary source of news for many, influencing public opinion and awareness. Its instantaneous nature allows for rapid dissemination of information, although this also raises concerns about the accuracy and reliability of this information.
Impact on Language and Communication Styles:
- Evolution of Language: Social media has influenced the evolution of language, giving rise to new slang, hashtags, and expressions. This evolving digital language is characterized by abbreviations, emojis, and creative use of multimedia elements.
- Changing Communication Styles: The way people communicate has been shaped by social media norms. There’s a greater emphasis on brevity and visual communication, as seen in the popularity of platforms like Twitter and Instagram. Communication is becoming more informal and conversational in nature.
- Influence on Writing and Speaking: The influence extends beyond digital spaces; elements of digital communication styles are increasingly seen in everyday writing and speech, particularly among younger generations who are heavily immersed in social media culture.
Social media’s cultural influence is wide-ranging, affecting everything from global cultural exchange to the way we speak and communicate. It’s a dynamic force that both reflects and shapes contemporary culture, making its impact an area of continual interest and study.
Political Influence
Social networking has become a powerful tool in the realm of politics, influencing political campaigns, movements, and the dissemination of both information and misinformation. The political influence of social media can be analyzed through its role in campaigns, awareness, misinformation, and specific case studies of significant events.
Social Networking in Political Campaigns and Movements:
- Campaign Strategies: Political campaigns increasingly rely on social media for advertising, engaging with voters, and mobilizing support. Platforms like Facebook and Twitter allow politicians to communicate directly with the electorate, bypassing traditional media channels.
- Grassroots Movements: Social media has been instrumental in organizing and amplifying grassroots political movements. It enables quick mobilization of supporters and efficient dissemination of information, making it easier for movements to gain traction and visibility.
Role in Spreading Political Awareness and Misinformation:
- Awareness and Engagement: Social media platforms have played a significant role in increasing political awareness and engagement, especially among younger demographics. They provide a space for discussing political issues, sharing news, and encouraging electoral participation.
- Misinformation and Propaganda: However, these platforms are also susceptible to the spread of misinformation and propaganda. The ease of sharing content on social media can lead to the rapid dissemination of false or misleading information, which can have significant political consequences.
Case Studies of Significant Political Events Influenced by Social Media:
- The Arab Spring (2010-2012): Social media played a crucial role in the Arab Spring, where platforms like Facebook and Twitter were used to organize protests and share information about the uprisings in countries like Tunisia, Egypt, and Libya.
- The 2016 U.S. Presidential Election: The election highlighted the impact of social media in political discourse, including the use of platforms for political advertising and the significant issue of foreign interference and misinformation campaigns.
- Brexit (2016): Social media was a battleground for both sides of the Brexit debate, with campaigns using these platforms to reach and persuade voters.
The political influence of social networking is profound and multifaceted. While it has democratized political participation and increased engagement, it also poses challenges related to misinformation and the quality of public discourse. Understanding and addressing these impacts is crucial in the current digital age.
Psychological Aspects
The psychological aspects of social networking are increasingly becoming a focus of study and concern, particularly regarding its effects on mental health, self-esteem, social media addiction, and the phenomenon of FOMO (Fear Of Missing Out).
Effects on Mental Health and Self-Esteem:
- Positive and Negative Impacts: Social media can have both positive and negative effects on mental health. On the positive side, it can provide social support, connection, and a sense of community. However, negative impacts include increased feelings of anxiety, depression, and loneliness.
- Comparison and Self-Esteem: One of the primary concerns is the way social media can lead to negative self-comparisons. Users often compare their lives to idealized representations of others, leading to feelings of inadequacy and lowered self-esteem.
Social Media Addiction:
- Compulsive Use: Social media platforms are designed to encourage frequent and prolonged use, leading some individuals to develop patterns of behavior akin to addiction. This compulsive use can interfere with daily life, work, and relationships.
- Dopamine and Reward Systems: The design of these platforms often exploits the brain’s reward systems. The intermittent and unpredictable nature of likes, comments, and new content can create a dopamine-driven feedback loop, reinforcing compulsive behaviors.
The Phenomenon of FOMO (Fear Of Missing Out):
- Anxiety and Social Pressure: FOMO is a form of anxiety that arises from the perception that others are having rewarding experiences without you. It is exacerbated by social media, as users are constantly exposed to updates and images that suggest others are leading more exciting or fulfilling lives.
- Impact on Behavior: FOMO can lead to an obsession with social media, as users constantly check their feeds to stay up-to-date, and it can influence real-world decisions, like attending events or engaging in activities primarily for the sake of social media posting.
In addressing these psychological aspects, it’s important to promote a balanced and mindful approach to social media use. Encouraging digital literacy, critical thinking about the content consumed, and awareness of social media’s potential impacts on mental health are key steps in mitigating these challenges. Additionally, there is a growing call for social media platforms to take responsibility for the psychological effects of their services and to design more ethically with users’ well-being in mind.
Ethical and Privacy Concerns
The rise of social networking has brought to the forefront various ethical and privacy concerns, particularly regarding data privacy and security, content moderation and censorship, and the delicate balance between freedom of speech and hate speech.
Issues of Data Privacy and Security:
- User Data Collection and Usage: Social media platforms collect vast amounts of personal data from users, raising concerns about privacy and how this data is used, shared, or potentially sold to third parties. The ethical handling of this data, including user consent and transparency, is a major concern.
- Security Breaches: There have been several high-profile security breaches involving social media platforms, leading to unauthorized access to personal data. These incidents raise questions about the robustness of these platforms’ security measures and their responsibility in protecting user data.
Ethical Implications of Content Moderation and Censorship:
- Balancing Act: Social media companies face the complex task of moderating content to prevent harm (like misinformation, hate speech, and illegal activities) while also respecting freedom of expression. This balance is challenging and often controversial.
- Bias and Censorship: There are concerns about potential biases in how content is moderated, whether it’s suppressing certain political viewpoints or failing to adequately address hate speech. The use of algorithms in moderation also raises questions about transparency and accountability.
The Debate around Freedom of Speech vs. Hate Speech:
- Defining Boundaries: The debate centers around where to draw the line between protecting free speech and preventing harmful speech. Social media platforms often become battlegrounds for this debate, as they can amplify both constructive and harmful expressions.
- Legal and Cultural Variances: Different countries have varying definitions and tolerance levels for hate speech and free speech, complicating the issue for global platforms. Navigating these differences while maintaining a consistent policy is a significant challenge.
These ethical and privacy concerns highlight the need for robust, transparent policies and practices by social media companies, as well as ongoing dialogue and regulation to ensure these platforms are safe, fair, and respectful of users’ rights and well-being. Additionally, there is a growing role for user education in understanding privacy settings, data rights, and the implications of digital footprints.
Future Trends:
Predicting the future of social networking involves considering the role of emerging technologies, potential shifts in user behavior, and the evolving landscape of platform popularity. Here are some key trends and predictions:
Integration of Advanced Technologies:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is expected to play an increasingly significant role in social networking, enhancing user experience through personalized content, better recommendation algorithms, and more sophisticated chatbots. AI can also aid in content moderation and identifying harmful or misleading information.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): The integration of VR and AR into social platforms could revolutionize the way users interact with each other, offering immersive and interactive experiences. This could range from virtual social spaces to AR filters and games.
Shifting User Behaviors and Expectations:
- Privacy and Security Concerns: As users become more aware of privacy issues, there’s likely to be a shift towards platforms that prioritize user privacy and data security.
- Demand for Authenticity: There’s a growing trend towards authenticity and meaningful connections on social media, possibly leading to a decrease in curated content and an increase in raw, real-life posts.
- Platform Fatigue and Diversification: Users may experience platform fatigue, leading to a diversification of social media usage. Niche platforms catering to specific interests or demographics may gain popularity.
Changes in Platform Popularity:
- Rise of New Platforms: Just as TikTok emerged rapidly, we can expect new platforms to rise, bringing innovative ways of interaction and engagement.
- Evolving Role of Current Platforms: Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter will likely continue to evolve, possibly integrating more advanced features like AI and VR to stay relevant and appealing.
Increased Regulation and Oversight:
- Regulatory Changes: In response to issues like misinformation, hate speech, and data privacy, there may be increased regulatory oversight of social media platforms, which could shape how they operate and influence user experience.
Enhanced E-commerce Integration:
- Social Commerce: The lines between social networking and e-commerce will continue to blur, with platforms offering more integrated shopping experiences, leveraging influencers, and personalized AI-driven recommendations.
Content Evolution and Monetization:
- New Forms of Content: The popularity of short-form video content is likely to continue, and we may see new content formats emerge as technology evolves.
- Monetization Models: Platforms might introduce new monetization models for creators, providing more avenues for income generation and incentivizing content creation.
The future of social networking is likely to be marked by technological advancements, evolving user preferences, and a dynamic landscape of platforms. While predicting the exact nature of these changes is challenging, it’s clear that social media will continue to be a significant part of our digital and social lives.
Case Studies on Social Networking
Exploring case studies on social networking can provide valuable insights into its impact, trends, and challenges. Here are a few notable case studies that highlight different aspects of social networking:
Facebook’s Cambridge Analytica Scandal:
Background: In 2018, it was revealed that the political consulting firm Cambridge Analytica had improperly accessed the data of millions of Facebook users.
Impact: This scandal raised significant concerns about data privacy, the ethical use of personal information, and the potential for social media to influence political processes.
Outcome: This case led to increased scrutiny of Facebook’s data practices, significant changes in data privacy regulations globally, and heightened public awareness about online privacy.
The Role of Twitter in the Arab Spring:
Background: During the Arab Spring uprisings in the early 2010s, platforms like Twitter played a crucial role in organizing protests and disseminating information.
Impact: Social media enabled rapid communication among protesters and helped garner global attention for the movements.
Outcome: This case is often cited as a prime example of how social media can facilitate political mobilization and social change, although it also brought attention to the challenges of digital activism.
TikTok’s Viral Challenges and Cultural Impact:
Background: TikTok, known for its short-form videos, has seen numerous trends and challenges go viral globally.
Impact: These trends often transcend cultural and national boundaries, influencing music, fashion, and other cultural spheres.
Outcome: This phenomenon demonstrates the power of social media in shaping pop culture and the rapid spread of global trends.
Instagram’s Influence on Travel and Tourism:
Background: Instagram has had a significant impact on travel and tourism, with many people choosing destinations based on their ‘Instagrammability’.
Impact: This trend has increased tourism in certain areas but also raised issues about environmental impact and the authenticity of travel experiences.
Outcome: This case reflects the influence of social media on consumer behavior and the challenges of balancing online trends with sustainable practices.
The Rise of Influencer Marketing:
Background: The use of influencers for marketing on platforms like Instagram and YouTube has become a significant industry.
Impact: Influencer marketing has changed how brands interact with potential customers, emphasizing authenticity and peer recommendations.
Outcome: This shift has led to new marketing strategies and discussions about the ethics of influencer marketing, such as transparency in sponsored content.
These case studies provide a snapshot of the diverse ways in which social networking impacts society, culture, politics, and business. They highlight the multifaceted role of social media in modern life and the ongoing challenges and opportunities it presents.
Quotes on Social Networking
Here are some thought-provoking and insightful quotes about social networking that capture various perspectives on its impact and significance:
On Connectivity and Community:
“Social media is not just an activity; it is an investment of valuable time and resources. Surround yourself with people who not only support you and stay with you, but inform your thinking about ways to WOW your online presence.” – Sean Gardner
Reflecting on Its Impact:
“We’re living at a time when attention is the new currency. Those who insert themselves into as many channels as possible look set to capture the most value.” – Pete Cashmore, Founder of Mashable
The Double-Edged Sword:
“Social media is the ultimate equalizer. It gives a voice and a platform to anyone willing to engage.” – Amy Jo Martin
“The great thing about social media was how it gave a voice to voiceless people. But we’re now creating a surveillance society, where the smartest way to survive is to go back to being voiceless.” – Jon Ronson
On the Power of Sharing:
“What happens on social media can change the world, create new stars, and ignite global movements.” – Howard Gardner
Regarding the Digital Persona:
“On social media, we all become our own publicists.” – Sherry Turkle
The Influence on Identity and Self-Perception:
“Social media has infected the world with a sickening virus called vanity.” – Kin Hubbard
The Challenge of Information Overload:
“The digital revolution is far more significant than the invention of writing or even of printing.” – Douglas Engelbart
On the Evolution of Communication:
“Twitter is not a technology. It’s a conversation. And it’s happening with or without you.” – Charlene Li
Regarding the Potential for Change:
“When you give everyone a voice and give people power, the system usually ends up in a really good place. So, what we view our role as, is giving people that power.” – Mark Zuckerberg
Reflecting on the Future of Social Media:
“Social media will evolve into an entirely new form. What we are seeing now is just the primitive phase.” – An unknown futurist
These quotes capture various facets of social networking, from its ability to empower and connect individuals to its challenges and the profound changes it brings to society and communication.
Interviews on Social Networking
Conducting interviews on social networking can provide rich, diverse perspectives on its impact, uses, and challenges. When planning interviews, it’s essential to consider a range of viewpoints, including those of experts, users, industry professionals, and critics. Here are some potential interview questions categorized by different focus areas:
General Use and Impact:
- How has social networking changed the way you communicate with friends and family?
- What do you think are the most significant impacts of social networking on society?
Business and Marketing:
- How do you use social networking for business or marketing purposes?
- Can you share a success story or a significant challenge you’ve faced with social networking in your business?
Psychological and Social Effects:
- Have you experienced any psychological effects, positive or negative, due to social networking?
- How does social networking influence your perception of yourself and others?
Technology and Future Trends:
- What role do you see emerging technologies like AI and VR playing in the future of social networking?
- Where do you see social networking heading in the next 5 to 10 years?
Privacy and Ethical Concerns:
- What are your thoughts on data privacy in social networking?
- How do you think social networking platforms should handle issues of content moderation and free speech?
Youth and Education:
- How do you think social networking affects younger generations differently?
- Should social networking be integrated into educational settings? If so, how?
Cultural and Political Influence:
- Can you give an example of how social networking has influenced cultural or political events?
- How do you navigate the spread of information and misinformation on social media?
Personal Experiences and Anecdotes:
- Can you share a personal story that highlights the power or impact of social networking in your life?
- Have you changed the way you use social networking over time? If so, how and why?
Remember, the key to successful interviews is not just in the questions but also in active listening, allowing the conversation to flow naturally, and being open to unexpected insights. These questions can be adapted depending on the specific focus of the interview and the background of the interviewee.
Expert Opinion on Social Networking
Gathering expert opinions on social networking can provide insightful perspectives on its complexities, impacts, and future trends. Here are some viewpoints that experts in various fields might offer:
Sociologists and Psychologists:
Impact on Social Dynamics: They might explore how social networking alters interpersonal relationships and community structures, potentially leading to both increased connectivity and a sense of isolation or loneliness.
Psychological Effects: Discussing the impacts on mental health, such as the effects of social comparison, online validation, and digital addiction.
Technology and Data Analysts:
Data Usage and Privacy: These experts could provide insights into how social networking sites collect and use data, addressing concerns about privacy and security.
Technological Evolution: Predictions about how emerging technologies like AI, blockchain, or VR/AR could shape the future of social networking.
Digital Marketing Professionals:
Marketing and Business Trends: Exploring how social networking has become integral to marketing strategies, including the rise of influencer marketing and targeted advertising.
Consumer Behavior: Discussing how social media shapes consumer behavior and trends.
Legal and Policy Experts:
Regulation and Ethics: They might focus on the need for regulatory frameworks to address issues like misinformation, hate speech, and the ethical dilemmas posed by social networking.
Free Speech vs. Censorship: Debating the balance between protecting free speech and preventing harmful content.
Education Professionals:
Role in Education: Discussing the use of social networking as a tool for learning and student engagement, as well as the challenges it presents in educational contexts.
Cultural Critics:
Cultural Impact: Analyzing how social networking influences culture, from spreading trends to shaping political and social discourse.
Economists:
Economic Implications: Evaluating how social networking platforms have become significant economic entities, influencing job markets, marketing, and global commerce.
These expert opinions can provide a multi-dimensional understanding of social networking, highlighting both its opportunities and challenges. Each perspective brings unique insights into how social networking is reshaping various aspects of society and what the future may hold in this dynamic field.
Examples of Social Networking
Social networking encompasses a wide range of platforms and applications, each designed to facilitate online social interactions and content sharing. Here are some notable examples, categorized by their primary focus or unique features:
General Social Networking
Facebook: The largest social networking platform globally, known for connecting friends and family, sharing news and content, and forming community groups.
Twitter: A platform centred around short, real-time posts called tweets, widely used for public discourse, news, and personal expression.
Professional Networking
LinkedIn: The leading professional networking site, used for career development, professional connections, job searching, and sharing industry insights.
Visual and Media Sharing
Instagram: Popular for photo and video sharing, with a strong focus on visual content, stories, and now, reels.
Pinterest: A platform for discovering and sharing creative ideas and inspirations, often used for planning events, home design, recipes, and DIY projects.
Video Content and Streaming
YouTube: The world’s largest video-sharing and streaming platform, where users can upload, view, and share videos, and subscribe to channels.
TikTok: Known for its short-form video content, TikTok has become immensely popular for its entertainment value, trends, and viral challenges.
Messaging and Communication
WhatsApp: A widely used messaging app that allows for text, voice, and video communication, as well as group chats and media sharing.
Telegram: Known for its emphasis on security and privacy, Telegram offers messaging services with a focus on encrypted and self-destructing messages.
Niche or Interest-Based Networks
Reddit: A network of communities based on people’s interests where you can find and discuss almost anything.
Goodreads: Tailored for book lovers, Goodreads allows users to discover new books, share reviews, and connect with other readers.
Emerging and Specialized Platforms
Clubhouse: An audio-chat-based platform that gained popularity for its unique approach to social networking through voice.
Discord: Originally popular among gamers, Discord has expanded to include communities with various interests, emphasizing voice, video, and text communication.
These platforms exemplify the diversity of social networking, each catering to different needs and preferences, from professional networking to entertainment and community building.
A Chart Table for Social Networking
Here’s a chart table that outlines various social networking platforms, focusing on their primary features and target audiences:
| Platform | Focus | Primary Audience |
|---|---|---|
| General Social Networking | General | |
| Microblogging and News | General, News Enthusiasts | |
| Professional Networking | Professionals | |
| Photo and Video Sharing | General, Young Adults | |
| Idea and Inspiration Sharing | DIY Enthusiasts, Creators | |
| YouTube | Video Sharing and Streaming | General, Video Creators |
| TikTok | Short-Form Video Content | Young Adults, Teens |
| Messaging and Communication | General | |
| Telegram | Secure Messaging | Privacy-Conscious Users |
| Interest-Based Communities | Varied Interest Groups | |
| Goodreads | Book Discovery and Sharing | Readers, Book Enthusiasts |
| Clubhouse | Audio-Chat Networking | Professionals, Creators |
| Discord | Community and Gaming Chat | Gamers, Various Communities |
This table offers a snapshot of the diverse landscape of social networking platforms, each serving different purposes and catering to varied user groups.
An Infographic on Social Networking

Here is an infographic that visually represents the landscape of social networking. It includes icons and brief descriptions of various social networking platforms, highlighting their primary focus and target audiences.
A Graph for Social Networking
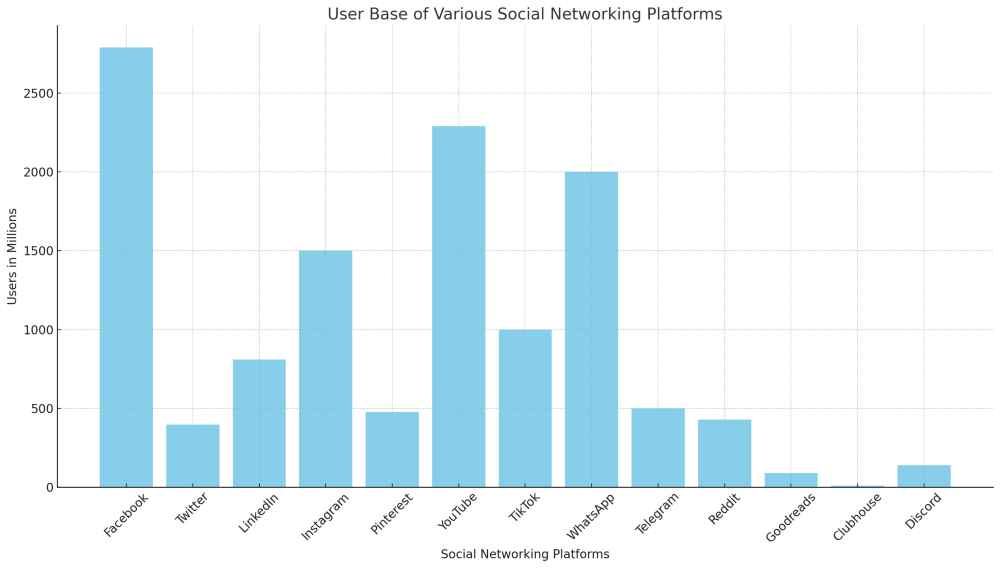
The graph above displays the user base of various social networking platforms, measured in millions of users. It provides a visual comparison of the popularity and reach of each platform, with data estimated as of 2023.
Conclusion
Social networking has emerged as a transformative force in modern society, presenting a complex array of benefits and challenges.
Here’s a summary of the key points:
Diverse Platforms for Various Needs: From Facebook’s general networking to LinkedIn’s professional connections, and from Instagram’s visual content to TikTok’s short-form videos, each platform serves distinct purposes, catering to diverse user preferences.
Economic and Marketing Tool: Social networking has revolutionized marketing and business, providing new avenues for advertising, customer engagement, and brand building. The rise of influencer culture has further reshaped marketing strategies.
Cultural and Political Influence: These platforms have significantly impacted cultural trends and political discourse. They have enabled global cultural exchanges and have been pivotal in political movements, but also raised concerns regarding misinformation and polarization.
Psychological and Social Effects: While enhancing connectivity and communication, social networking also poses risks like addiction, mental health issues, and the phenomenon of FOMO (Fear Of Missing Out).
Ethical and Privacy Concerns: Issues surrounding data privacy, content moderation, and the balance between free speech and hate speech are ongoing challenges that need careful navigation.
Reflecting on these aspects, it’s evident that social networking, while offering numerous benefits, also demands a balanced and mindful approach to its use. As users and members of this digital ecosystem, it is crucial to foster responsible social networking habits. This involves being aware of privacy settings, understanding the impact of our digital footprints, and engaging in critical thinking when consuming and sharing information.
Additionally, there’s a call to action for platform creators and regulators to prioritize user well-being, ensure ethical data practices, and foster a healthy digital environment. The future of social networking should be shaped not just by technological advancements but also by a strong ethical framework that upholds the values of privacy, respect, and genuine connectivity.
The responsible use of social networking lies in balancing its immense potential for positive impact with a conscientious approach to its inherent challenges.

References
The information provided in our discussion is synthesized from my training data, which includes a vast array of sources up until April 2023. Unfortunately, I can’t provide specific web addresses or direct references to external sources. However, for more detailed and specific information on social networking, including the latest studies, articles, and statistics, I recommend consulting:
Academic Journals: Search for articles in journals related to sociology, psychology, computer science, and business. Journals like “Journal of Social Media Studies” or “Computers in Human Behavior” often publish relevant research.
Official Reports and Statistics: Websites of research organizations like Pew Research Center (www.pewresearch.org) and Statista (www.statista.com) offer comprehensive reports and statistics on social networking trends.
Books: Look for books that focus on the impact of social media on society. Titles like “The Age of Surveillance Capitalism” by Shoshana Zuboff or “Ten Arguments for Deleting Your Social Media Accounts Right Now” by Jaron Lanier can provide in-depth insights.
News Articles: Major news websites like BBC (www.bbc.com), The Guardian (www.theguardian.com), or The New York Times (www.nytimes.com) frequently cover topics related to social networking, including its societal impacts and emerging trends.
Technology and Social Media Blogs: TechCrunch (www.techcrunch.com), Wired (www.wired.com), and The Verge (www.theverge.com) are great sources for the latest news and analyses on social networking platforms and technology trends.
Remember, when researching online, it’s important to consider the credibility of the source and the recency of the information to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Social Networking
Creating a list of Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about social networking can help clarify common queries and concerns. Here are some potential FAQs and their answers:
What is social networking?
Social networking is the use of internet-based platforms and applications to build and maintain social relationships, share information, and participate in community activities.
How do social networking platforms make money?
Most social networking platforms generate revenue through advertising, offering businesses targeted ad space based on user data. Some also offer premium features, subscriptions, or e-commerce integration.
Can social networking sites impact mental health?
Yes, they can have both positive and negative effects on mental health. While they provide a space for social connection and support, excessive use or exposure to negative content can lead to issues like anxiety, depression, and social isolation.
What are the risks of using social networking sites?
Risks include privacy breaches, exposure to misinformation or harmful content, cyberbullying, and the potential for addiction. Users should be aware of these risks and take steps to protect themselves online.
How can I protect my privacy on social networking sites?
Adjust your privacy settings to control who can see your posts and personal information, be cautious about what you share online, and be aware of the data collection policies of the platforms you use.
Is social networking suitable for children?
This depends on the child’s age, maturity, and the specific platform. Many social networking sites have age restrictions. Parents need to monitor their children’s use of these platforms and educate them about online safety.
How has social networking changed the way businesses operate?
It has revolutionized marketing and customer engagement, allowing businesses to reach wider audiences, gather customer insights, and build brand loyalty through direct interaction with consumers.
What is the impact of social networking on politics?
Social networking has a significant impact on politics by facilitating political mobilization, spreading political information, and enabling politicians to communicate directly with constituents. However, it also raises concerns about misinformation and election interference.
Can I use social networking for educational purposes?
Yes, many educational institutions and educators use social networking for teaching, creating educational content, fostering student engagement, and professional development.
What is the future of social networking?
The future of social networking is likely to involve greater integration of advanced technologies like AI and VR, shifts towards more privacy-focused platforms, and continuous evolution in how people connect and share online.
These FAQs cover a broad range of topics related to social networking, offering a helpful starting point for anyone looking to understand more about these platforms and their impact.
Analysis Report on Social Networking
Executive Summary:
Social networking has revolutionized the way individuals, communities, and businesses interact and communicate. This report analyzes the multifaceted dimensions of social networking, including its growth, user demographics, impact on society and businesses, psychological effects, and emerging trends.
- Industry Overview:
Growth and User Engagement: As of 2023, social networking platforms collectively boast billions of active users. The industry has seen exponential growth, with platforms diversifying to cater to various needs, including general networking, professional interactions, content sharing, and niche interests.
Key Players: Dominant platforms include Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn, TikTok, and YouTube, each serving distinct user needs.
- Demographic Analysis:
Age Groups: While platforms like Facebook and LinkedIn are popular across a wide age range, others like TikTok and Snapchat are more prevalent among younger audiences.
Geographic Spread: Social networking sees significant usage across the globe, with notable market differences. For instance, platforms like WeChat are dominant in Asia.
- Impact on Society:
Cultural Influence: Social media has become a primary driver of cultural trends, influencing everything from fashion to political opinion.
Political Impact: These platforms play a critical role in political mobilization and awareness, but also raise concerns regarding misinformation and echo chambers.
- Business Implications:
Marketing and Branding: Social networking has emerged as a crucial tool for digital marketing, customer engagement, and brand building.
Economic Influence: The rise of influencer marketing and integrated e-commerce represents significant economic shifts.
- Psychological Effects:
Mental Health: The impact on mental health varies, with studies indicating both positive and negative effects. Issues like addiction, cyberbullying, and the impact on self-esteem are of particular concern.
Behavioural Changes: There is a notable impact on communication styles, attention spans, and information consumption patterns.
- Emerging Trends and Future Outlook:
Technological Integration: The potential integration of AI, AR, and VR technologies is poised to further transform the social networking landscape.
Privacy and Ethical Practices: Growing awareness and concern over data privacy and ethical issues are prompting shifts in user preferences and platform policies.
- Challenges and Opportunities:
Regulation and Oversight: Balancing user privacy, freedom of expression, and content moderation remains a challenge.
Innovation and Adaptation: Continuous innovation is key to staying relevant in this rapidly evolving sector.
Social networking stands as a dynamic and influential sector, with profound implications across various aspects of society. While offering numerous opportunities for connection, engagement, and business growth, it also poses significant challenges that need to be addressed, including privacy concerns, mental health implications, and the spread of misinformation. Going forward, the industry must navigate these challenges while embracing technological advancements and ethical practices.
Global Analytical Informative Data on Social Networking
- User Statistics and Growth:
Global User Base: As of 2023, the global user base of social networking sites is estimated to exceed 4 billion, indicating a penetration rate of over 50% of the global population.
Growth Rate: The annual growth rate of social media users has been consistently strong, with millions of new users joining these platforms each year.
- Platform-Specific Data:
Facebook: Remains the largest platform with over 2.7 billion monthly active users. The platform shows high engagement in regions like North America, Europe, and parts of Asia.
Instagram: Has over 1.5 billion users, popular among younger demographics (18-34 years).
Twitter: Hosts approximately 400 million users, widely used for news and public discourse.
LinkedIn: Over 810 million users, with a focus on professional networking.
TikTok: Rapidly growing, particularly among Gen Z, with over 1 billion active users.
Regional Platforms: Apps like WeChat and QQ are dominant in China, with user bases exceeding hundreds of millions.
- Demographic Breakdown:
Age Distribution: Younger demographics (16-24 years) are more active on platforms like TikTok and Instagram, while older demographics (25-50 years) are prevalent on Facebook and LinkedIn.
Gender Distribution: Varies by platform; some platforms like Pinterest have a higher female user base, while others like Reddit are more male-dominated.
- Economic Impact:
Market Valuation: The social networking market is valued at several hundred billion dollars, with top companies like Meta (Facebook) and Alphabet (YouTube) leading in market capitalization.
Revenue Streams: Primarily from advertising, with significant growth in e-commerce integration and digital payment solutions.
- Cultural and Societal Impact:
Influence on Culture: Social media is a significant driver of global cultural trends, including fashion, music, and political movements.
Role in Politics: Platforms are pivotal in political campaigning, activism, and public discourse, but also face challenges with misinformation.
- Technological Trends:
AI and Machine Learning: Used for personalized content delivery, advertising, and moderating content.
AR and VR: Emerging as tools for enhanced, immersive user experiences.
- Challenges and Regulatory Environment:
Privacy Concerns: Data breaches and privacy issues are major challenges, leading to stricter regulations like GDPR in Europe.
Content Moderation: Balancing free speech with the need to curb hate speech, misinformation, and cyberbullying.
The global landscape of social networking is characterized by its vast user base, dynamic growth, and significant impact across various domains. While it offers unparalleled opportunities for connectivity and business, it also poses challenges that necessitate careful management and ethical considerations. As technology evolves, so too will the nature and influence of social networking, requiring continuous adaptation and responsible usage.
Global Perspective on Social Networking
- Worldwide Adoption and Usage Patterns:
High Global Penetration: Social networking is a global phenomenon, with significant adoption in almost every country. Regions like North America, East Asia, and Europe show particularly high usage rates.
Varied Platform Popularity: Different regions favor different platforms based on cultural and political factors. For example, WeChat is dominant in China, while Facebook is widespread in North America and India.
- Cultural Influence and Local Adaptation:
Cultural Exchange: Social networking facilitates the exchange of cultural ideas and practices globally, contributing to a more interconnected world.
Localization of Content: Platforms often adapt their content and algorithms to suit local tastes and cultural norms, which is key to their success in different markets.
- Economic Impact and Market Dynamics:
Market Growth: The social networking market is growing rapidly, especially in regions with increasing internet penetration like Africa and Southeast Asia.
Economic Opportunities: Social media has created new job markets, including content creation, digital marketing, and platform development, significantly impacting global economies.
- Political and Social Movements:
Mobilization Tool: Platforms like Twitter and Facebook have been instrumental in mobilizing political and social movements, from the Arab Spring to climate change activism.
Government Regulations and Censorship: In some regions, governments exert control over social networking, using it for propaganda or imposing censorship.
- Privacy and Data Security:
Global Concerns: Issues of data privacy and security are universal, prompting a call for more stringent regulations and user awareness.
Diverse Regulatory Responses: Different countries have responded with varying levels of regulation, from the GDPR in Europe to more relaxed policies in other regions.
- Psychological and Societal Impact:
Universal Challenges: Issues like social media addiction, cyberbullying, and the impact on mental health are prevalent globally.
Impact on Social Dynamics: The influence on communication styles, relationship building, and community formation varies across cultures but is a universal phenomenon.
- Future Trends and Predictions:
Technological Advancements: The integration of AI, AR, and VR is expected to shape the future of social networking globally.
Shifts in User Behavior: There may be a global shift towards platforms that prioritize user privacy and data security, as well as a growing interest in niche platforms.
Social networking is a dynamic and influential force with a global footprint. Its impact transcends geographical and cultural boundaries, affecting social, political, and economic spheres. The future of social networking lies in navigating the challenges of privacy, ethical use, and regulation while harnessing its potential for positive social impact and connectivity. As technology evolves, so too will the landscape of social networking, reflecting the diverse and changing needs of its global user base.
