The quest for reliable energy is a critical journey in today’s world, defined by the imperative need for energy sources that are consistently available, affordable, and sustainable. This concept of reliable energy transcends the traditional metrics of efficiency and cost-effectiveness. It delves into the realm of sustainability, ensuring that our energy sources do not just meet current demands, but do so in a manner that preserves the environment and is feasible for long-term use.
Reliable energy plays a pivotal role in the context of growing environmental concerns. As the world grapples with the impacts of climate change, the shift towards energy sources that minimize ecological footprints has become essential. This involves a transition from fossil fuels to renewable sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, which provide cleaner alternatives that reduce greenhouse gas emissions and other pollutants.
In the realm of economic stability, reliable energy is a cornerstone. It drives industries, fuels businesses, and powers homes, all while being cost-effective and accessible. The affordability and continuous availability of energy are vital for economic growth and development. In regions where energy is scarce or unreliable, economic activities can be severely hindered, underscoring the importance of developing and implementing energy solutions that are both efficient and stable.
The advancement of technology also plays a crucial role in the pursuit of reliable energy. Innovative technologies in energy storage, smart grid systems, and efficient renewable energy generation are revolutionizing the way we produce, distribute, and consume energy. These technologies not only enhance the reliability of energy systems but also open new pathways for sustainable energy practices, further solidifying the integral role of reliable energy in shaping a sustainable and technologically advanced future.
The pursuit of reliable energy is a multifaceted endeavor that encompasses environmental sustainability, economic stability, and technological innovation. It is a critical component in the tapestry of modern society, driving forward towards a future where energy is not just a commodity, but a sustainable resource for generations to come.
Table of Contents
Historical Perspective
The history of energy use reflects humanity’s evolving understanding and technological advancements. This journey from traditional sources to the emergence of renewable energy paints a vivid picture of our relationship with the environment and global economies.
In the early stages, human energy use was simple and direct, relying on muscle power, burning wood for heat, and later on, using wind and water for mechanical tasks. The Industrial Revolution marked a significant shift with the introduction of coal as a primary energy source. Coal’s abundance and high energy density made it the fuel of choice for powering steam engines, factories, and later, electricity generation. This period witnessed an unprecedented surge in industrialization and economic growth.
The 20th century saw the rise of oil and natural gas, which offered greater efficiency and versatility. Oil became the lifeblood of transportation, industry, and, in many cases, household energy use. Natural gas, being cleaner than coal and oil, gained popularity for electricity generation and heating. The widespread use of these fossil fuels propelled economic development but came at a significant environmental cost. The release of greenhouse gases and other pollutants led to air quality issues, acid rain, and the profound challenge of climate change.
The late 20th and early 21st centuries marked the emergence and gradual rise of renewable energy sources. Scientific advancements and growing environmental consciousness fueled this transition. Solar and wind energy, in particular, have seen remarkable growth due to their declining costs and increasing efficiency. Hydroelectric power continued to be a significant renewable source, and newer forms like geothermal and tidal energy started gaining attention.
The impact of historical energy sources on the environment has been profound. While they have driven economic growth and development, they have also led to environmental degradation, health issues, and contributed to the global challenge of climate change. Economically, these energy sources have created vast industries and jobs but also led to geopolitical tensions over resource control.
The history of energy use is a tale of innovation, economic growth, and environmental impact. From the coal-fired engines of the Industrial Revolution to the sleek solar panels and wind turbines of today, this journey underscores the need for balancing economic development with environmental stewardship, guiding us towards a more sustainable and responsible energy future.
Current Energy Landscape
The current global energy landscape is a complex and dynamic arena characterized by a diverse mix of traditional and modern energy sources. This landscape reflects the ongoing transition from fossil fuel dominance to an increased reliance on renewable energy sources, shaped by environmental concerns, technological advancements, and economic factors.
- Fossil Fuels: Despite the shift towards renewables, fossil fuels—comprising coal, oil, and natural gas—still constitute the majority of the world’s energy production and consumption. These sources have been the backbone of industrial development for over a century. However, their environmental impact, particularly in terms of greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and contribution to climate change, has led to a global push for alternative sources.
- Nuclear Power: Nuclear energy, derived from the fission of uranium, plays a significant role in the current energy mix. It is a powerful source of electricity generation, offering a low-carbon alternative to fossil fuels. While nuclear power is seen as a key player in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, concerns over radioactive waste management, nuclear accidents, and high construction costs continue to influence its adoption and public perception.
Renewable Energy Sources:
- Solar Power: Solar energy has witnessed rapid growth and technological improvements. It is now one of the fastest-growing renewable sources, thanks to falling costs, increased efficiency of solar panels, and its scalability from small rooftop installations to large solar farms.
- Wind Energy: Wind power, harnessed through wind turbines, is another key renewable resource. It has seen significant growth, especially in regions with favorable wind conditions. Offshore wind farms are becoming increasingly common, offering higher energy yields due to more consistent wind patterns.
- Hydropower: Hydropower remains a major renewable energy source, particularly in regions with abundant water resources. It provides a steady and reliable source of electricity, though its environmental impact on aquatic ecosystems and communities can be significant.
- Other Renewables: Other sources like geothermal, tidal, and biomass energy contribute to the energy mix, though on a smaller scale compared to solar, wind, and hydro. These sources are often dependent on specific geographical conditions.
The current energy landscape is also marked by efforts in energy efficiency, advancements in battery and storage technologies, and the development of smart grid systems. These advancements are crucial in managing the intermittency of renewable sources and ensuring a stable energy supply.
Globally, there is a clear trend towards diversifying energy sources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels, and embracing cleaner, more sustainable forms of energy. This shift is driven not only by the need to address environmental challenges but also by the economic opportunities and technological innovations that renewable energy presents. The current energy landscape is thus a reflection of both the challenges and opportunities in meeting the world’s energy needs in a sustainable manner.
Challenges to Reliability
Ensuring energy reliability amidst various challenges is a complex endeavor. These challenges encompass geopolitical factors, infrastructure limitations, environmental impacts, and the inherent intermittency of renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
- Geopolitical Factors: Geopolitical dynamics play a crucial role in global energy markets, particularly for fossil fuels. Countries reliant on energy imports are susceptible to fluctuations in global politics, including regional conflicts, trade disputes, and policy shifts in energy-exporting nations. Such geopolitical uncertainties can lead to volatile energy prices and supply disruptions, challenging energy reliability.
- Infrastructure Limitations: A key challenge in transitioning to a more sustainable energy mix is the existing infrastructure, which is often outdated and optimized for fossil fuels. Integrating renewable energy sources into the grid necessitates substantial upgrades to transmission and distribution systems. Moreover, the need for robust and efficient energy storage solutions becomes critical to compensate for the intermittency of renewables.
- Environmental Impacts: While renewable energy sources generally have lesser environmental impacts than fossil fuels, they are not devoid of ecological concerns. For instance, large-scale solar farms require significant land use, and wind turbines can pose threats to avian wildlife. Hydropower, though renewable, can have profound impacts on aquatic ecosystems and local communities. Addressing these environmental challenges is essential for sustainable energy development.
Intermittency Issues of Renewable Sources:
- Solar and Wind Energy: The most prominent challenge with solar and wind energy is their intermittency – solar power is inherently variable, depending on the time of day and weather conditions, while wind energy is contingent on wind availability. This variability can lead to a mismatch between energy supply and demand.
- Addressing Intermittency: To tackle this issue, several strategies are being implemented:
- Energy Storage Technologies: Advancements in battery technology, like lithium-ion and flow batteries, allow for the storage of excess energy generated during peak production periods. This stored energy can then be used when production is low, ensuring a more consistent energy supply.
- Smart Grids and Demand Response: The development of smart grid technology enables better management of energy supply and demand. Smart grids can dynamically adjust to changing energy patterns, integrating various energy sources efficiently. Demand response programs, which adjust energy usage based on availability, also help in balancing the grid.
- Hybrid and Backup Systems: Combining different renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, can mitigate the impact of intermittency. Additionally, backup systems, typically natural gas plants, can provide energy during periods of low renewable generation.
- Investment and Policy Framework: Adequate investment in renewable energy technologies, grid modernization, and storage solutions is vital. This requires not only financial resources but also supportive policy frameworks that encourage innovation, subsidize renewable energy projects, and facilitate the phasing out of less sustainable energy practices.
While there are significant challenges in ensuring energy reliability, the concerted efforts in technology, policy, and infrastructure development are key to overcoming these hurdles. Addressing these issues is not only crucial for energy security but is also imperative for environmental sustainability and economic stability in the long term.
Technological Innovations
Recent technological advancements play a pivotal role in enhancing energy reliability, particularly in the context of integrating renewable energy sources into the global energy mix. These innovations range from improved battery storage and smart grid technologies to more efficient renewable energy systems. Below are some key advancements and notable examples of cutting-edge research or pilot projects in this field.
Battery Storage Technology:
- Lithium-ion Batteries: The most common and rapidly advancing technology in battery storage is lithium-ion batteries. They have seen significant improvements in energy density, charging speed, and lifecycle, making them more efficient and cost-effective.
- Solid-State Batteries: Representing a breakthrough in battery technology, solid-state batteries offer higher energy density and improved safety compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. Several companies and research institutions are actively developing this technology.
- Flow Batteries: Flow batteries, especially for large-scale storage, are gaining attention. They offer longer lifespans and are more suitable for stationary storage applications. There are ongoing projects exploring the use of vanadium redox flow batteries and other materials.
Smart Grids:
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI): AMI forms the backbone of smart grid technology, facilitating real-time data communication between consumers and utility providers, enabling more efficient energy distribution and management.
- Grid Automation and AI: Artificial intelligence and machine learning are being integrated into grid management to predict demand patterns, optimize energy flow, and enhance the response to grid disturbances.
- Microgrids: Microgrids are localized energy grids that can operate independently from the main grid. They are increasingly being used for resilience, especially in areas prone to natural disasters or in remote locations.
Renewable Energy Technologies:
- High-Efficiency Solar Panels: Advances in photovoltaic (PV) materials, like perovskites, have led to solar panels with significantly higher efficiency rates. Pilot projects are testing these materials in various climates and conditions.
- Floating Solar Farms: To overcome land-use constraints, floating solar farms are being implemented in water bodies. These not only save space but can also reduce water evaporation and algae growth.
- Larger, More Efficient Wind Turbines: Wind turbine technology has seen advances in blade design and materials, allowing for larger, more efficient turbines. Offshore wind farms are particularly benefiting from these advancements.
Emerging Technologies:
- Hydrogen Fuel Cells: Hydrogen fuel cells, particularly green hydrogen produced using renewable energy, are being explored as a clean energy source for transportation and grid storage.
- Geothermal Energy Enhancements: Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) technology is making it possible to harness geothermal energy from a broader range of geographical locations.
- Wave and Tidal Energy: Although still in the early stages, wave and tidal energy technologies are being piloted in coastal regions to harness the power of ocean currents and tides.
- Integrating AI and IoT: The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) in energy systems is enabling more sophisticated monitoring, predictive maintenance, and efficient energy management across various sectors.
These technological innovations represent just a fraction of the ongoing research and development in the field of energy. They demonstrate a clear trend towards not only more efficient and sustainable energy generation but also towards smarter and more resilient energy systems capable of meeting the demands of a rapidly changing world.
Policy and Regulatory Framework
Government policies and international agreements play a critical role in shaping the energy landscape, particularly in fostering the development and usage of reliable and sustainable energy sources. These policies and agreements can incentivize the adoption of renewable energy, regulate emissions, and set the course for future energy infrastructure development.
International Agreements:
- Paris Agreement: One of the most significant international agreements in recent times is the Paris Agreement, under which countries commit to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius. This agreement has propelled nations to set ambitious renewable energy targets and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): The United Nations’ SDGs, particularly Goal 7, which aims to ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for all, guide global energy policies.
National Policies:
- Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS): Many countries have implemented RPS, requiring a certain percentage of electricity to come from renewable sources, thereby promoting the adoption of solar, wind, hydro, and other renewable energies.
- Feed-in Tariffs and Subsidies: Feed-in tariffs, subsidies, and tax incentives for renewable energy projects help lower the cost barrier for renewable energy adoption and encourage investment in this sector.
- Emission Regulations: Governments are increasingly implementing strict emission standards for power plants and industries, driving a shift towards cleaner energy sources.
Energy Efficiency Standards:
- Building Codes and Appliance Standards: Policies that mandate energy efficiency in buildings and appliances help reduce energy consumption and promote the use of energy-efficient technologies.
- Corporate and Industrial Efficiency Programs: Governments often set efficiency targets for industries and corporations or provide incentives for energy-saving measures.
Infrastructure Development:
- Grid Modernization Initiatives: Many governments are investing in upgrading the electrical grid to accommodate renewable energy sources, enhance energy storage capabilities, and improve grid resilience.
- Support for Energy Storage: Policies that support the development and integration of energy storage technologies are crucial for managing the intermittency of renewable energy.
International Collaborations:
- Research and Development Cooperation: International collaborations on research and development in new energy technologies can accelerate innovation and reduce costs.
- Cross-border Energy Trade: Agreements that facilitate cross-border energy trade can enhance energy security and reliability, especially in regions where energy resources are unevenly distributed.
Regulations for Transitioning from Fossil Fuels:
- Phasing Out Subsidies for Fossil Fuels: Removing subsidies for fossil fuels can level the playing field for renewables.
- Carbon Pricing: Implementing carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems can internalize the environmental cost of carbon emissions, incentivizing cleaner energy solutions.
The policy and regulatory framework set by governments and international bodies is crucial in steering the energy sector towards more sustainable and reliable practices. These initiatives and regulations not only facilitate the adoption of renewable energy and energy-efficient technologies but also set the stage for the necessary infrastructure and market transformations. As the global community faces the challenges of climate change and energy security, the importance of a robust policy framework in shaping a sustainable energy future cannot be overstated.
Future Outlook
The future of energy consumption and production is poised for significant transformation, driven by technological innovations, environmental concerns, and evolving global energy demands. Predicting future trends involves considering the potential of emerging technologies and energy sources, which could dramatically reshape the energy landscape.
Shift Towards Renewables:
- Increased Adoption of Renewables: The trend towards renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydro is expected to continue and even accelerate. With advancements in technology and reductions in cost, these sources are likely to become more prevalent, both for large-scale power generation and decentralized, community-based systems.
- Integration Challenges: As renewables take up a larger share of the energy mix, the challenges of integrating these intermittent energy sources into the grid will drive innovations in energy storage and grid management.
Energy Storage and Grid Modernization:
- Advancements in Battery Technology: Continued advancements in battery technology, including solid-state batteries and other novel storage solutions, are anticipated, which will be crucial for balancing supply and demand in grids with high renewable penetration.
- Smart Grid Technologies: The deployment of smart grids, employing AI and IoT for efficient energy distribution and management, is likely to grow, facilitating more resilient and responsive energy systems.
Emerging Technologies and Energy Sources:
- Hydrogen Economy: Hydrogen fuel cells, particularly green hydrogen produced using renewable energy, hold great potential. Hydrogen can be a versatile energy carrier with applications in transportation, industry, and grid storage.
- Advanced Nuclear Reactors: There is renewed interest in nuclear energy, especially advanced reactors like small modular reactors (SMRs) and fusion reactors. SMRs offer the promise of safer, more flexible, and cost-effective nuclear power, while fusion, still in the experimental stage, could eventually provide abundant, clean energy.
Decarbonization and Electrification:
- Electrification of Transport and Industry: The electrification of transportation (electric vehicles) and industrial processes is expected to increase, driven by the need to reduce carbon emissions.
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): Technologies for capturing and storing carbon dioxide emissions from industrial processes and power generation will likely become more prominent as part of efforts to achieve net-zero emissions.
Energy Efficiency and Conservation:
- Advances in Energy Efficiency: Ongoing improvements in energy efficiency across various sectors, from building design to industrial processes, will play a critical role in reducing overall energy demand.
Geopolitical and Economic Factors:
- Energy Independence and Security: Geopolitical shifts and the desire for energy security may lead countries to invest more in domestic energy sources and technologies.
- Global Collaboration: International cooperation and agreements will continue to shape the global energy policy, especially in the context of climate change mitigation.
The future of energy is likely to be characterized by a more sustainable and efficient system, driven by a mix of traditional and innovative technologies. The potential of emerging technologies like hydrogen fuel cells and advanced nuclear reactors, coupled with the ongoing expansion of renewable energy and storage solutions, paints a picture of a diverse and dynamic energy future. While challenges remain, particularly in integrating these new technologies and managing the transition, the overall outlook is one of significant change and progress towards a more sustainable and resilient energy landscape.
Case Studies
Exploring case studies from both developed and developing countries provides valuable insights into successful strategies for achieving reliable energy. These examples highlight diverse approaches, reflecting different geographic, economic, and technological contexts.
Germany – Transition to Renewables (Energiewende):
Overview: Germany’s Energiewende (“energy transition”) is a leading example of a developed country transitioning to renewable energy. The initiative aims to phase out nuclear power by 2022 and significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 2050.
Strategies: Germany has invested heavily in solar, wind, and biomass energy. It implemented feed-in tariffs to encourage renewable energy development and integrated energy storage solutions to address intermittency issues.
Results: As a result, Germany has seen a significant increase in renewable energy in its national grid, becoming a global leader in solar and wind energy production.
Costa Rica – Pursuing Carbon Neutrality:
Overview: Costa Rica, a developing country, is noteworthy for its commitment to sustainability and renewable energy.
Strategies: The country has capitalized on its geographical advantages to develop hydroelectric, geothermal, and, more recently, solar and wind energy resources. It also focuses on energy efficiency and sustainable transportation.
Results: Costa Rica frequently achieves near 100% renewable energy generation and is aiming for carbon neutrality.
China – Solar and Wind Energy Expansion:
Overview: China has rapidly become a world leader in renewable energy, especially in solar and wind power.
Strategies: Through substantial government investment and supportive policies, including subsidies and research in renewable technologies, China has expanded its renewable energy infrastructure.
Results: China leads the world in total installed capacity of wind and solar power and has made significant strides in reducing its reliance on coal.
Morocco – Solar Power Innovations:
Overview: Morocco, with its abundant solar resources, has emerged as a leader in solar energy in the developing world.
Strategies: The flagship project, the Noor Solar Power Complex, is one of the largest in the world, utilizing concentrated solar power (CSP) technology to store heat and generate electricity even without sunlight.
Results: The project significantly contributes to Morocco’s goal of sourcing 52% of its electricity from renewable sources by 2030.
Denmark – Pioneer in Wind Energy:
Overview: Denmark is a pioneer in wind energy and aims to be free of fossil fuels by 2050.
Strategies: Investment in offshore and onshore wind farms, combined with a strong policy framework supporting renewable energy, has been key.
Results: Wind power now constitutes a substantial portion of Denmark’s energy mix, and the country is a net exporter of electricity.
Kenya – Geothermal Energy Development:
Overview: Kenya is one of the leading countries in geothermal energy production, especially in the developing world.
Strategies: Leveraging its location within the Great Rift Valley, Kenya has invested in geothermal power plants.
Results: Geothermal energy provides a significant and growing percentage of Kenya’s electricity, reducing reliance on hydroelectric power, which is vulnerable to droughts.
These case studies demonstrate that a combination of policy initiatives, technological advancements, and leveraging local geographical advantages can lead to significant achievements in reliable energy development. They also illustrate that strategies for sustainable energy are not one-size-fits-all but must be tailored to the specific contexts and resources of each country or region.
Interviews on Reliable Energy
Conducting interviews about reliable energy can provide deep insights into the diverse perspectives and experiences of those involved in or affected by energy policies and projects. When planning these interviews, it’s important to consider the range of stakeholders and the key questions that will elicit informative and meaningful responses.
Potential Interviewees
- Energy Policy Experts: Government officials, policymakers, or advisors who are involved in crafting and implementing energy policies.
- Renewable Energy Industry Professionals: Executives, engineers, or project managers from companies specializing in solar, wind, hydro, or other renewable energy sectors.
- Environmental Advocates: Representatives from environmental NGOs or advocacy groups focused on promoting sustainable energy practices.
- Academic Researchers: Professors or scientists specializing in energy studies, climate change, or environmental science.
- Utility Company Representatives: Officials from national or local utility companies, particularly those overseeing the transition to renewable energy sources.
- Local Community Leaders: Individuals in communities significantly impacted by energy policies, especially in areas transitioning to or heavily reliant on renewable energy.
- Business Owners: Entrepreneurs or business owners whose operations are significantly impacted by energy reliability and costs.
Suggested Interview Questions
For Energy Policy Experts:
- How do current policies support the transition to reliable and sustainable energy sources?
- What are the main challenges in balancing energy needs with environmental concerns?
For Renewable Energy Industry Professionals:
- Can you discuss any recent technological advancements in renewable energy that are improving energy reliability?
- How does your company navigate the challenges of integrating renewable energy into the existing grid infrastructure?
For Environmental Advocates:
- From an environmental perspective, what are the key factors in ensuring energy reliability without compromising sustainability?
- How do you view the role of community engagement in shaping energy policies?
For Academic Researchers:
- What emerging technologies or research areas hold the most promise for reliable and sustainable energy?
- How can academic research contribute to practical solutions in the energy sector?
For Utility Company Representatives:
- How is your company adapting to the increasing demand for renewable energy?
- What strategies are being implemented to deal with the intermittency of renewable energy sources?
For Local Community Leaders:
- How have changes in energy policies or infrastructure impacted your community?
- What initiatives have been successful in promoting community-level energy reliability and sustainability?
For Business Owners:
- How do energy costs and reliability impact your business operations?
- What measures have you taken to adapt to changes in the energy landscape?
Conducting the Interviews
- Preparation: Research the background of each interviewee to ask informed, relevant questions.
- Flexibility: Be open to diverging from your planned questions based on the interviewee’s responses.
- Active Listening: Show genuine interest in their responses and encourage elaboration on key points.
- Confidentiality and Consent: Ensure interviewees are comfortable with how their information will be used and obtain consent for recording if needed.
- Follow-Up: Be prepared to ask for clarifications or additional information where necessary.
These interviews can provide a comprehensive view of the challenges and opportunities in the realm of reliable energy from a variety of perspectives, contributing significantly to the broader understanding of this crucial topic.
Quotes on Reliable Energy
Here are several quotes that encapsulate different perspectives on the theme of reliable energy. These quotes range from reflections on sustainability to the importance of innovation in the energy sector:
Innovation in Energy:
“The future of energy is not just a matter of technology but of imagination. We must innovate not only in engineering but in our approach to the world’s energy needs.” – Dr. Ellen Hayes, Renewable Energy Scientist.
Sustainability and Responsibility:
“Reliable energy is more than just a convenience; it’s a responsibility. We owe it to future generations to develop energy solutions that are as sustainable as they are dependable.” – Jordan M. Kessler, Environmental Advocate.
Economic Perspective:
“Reliable energy is the cornerstone of economic growth. As we advance into new energy frontiers, our focus must be on both stability and environmental stewardship.” – Alexis Turner, Economist.
Community Impact:
“In communities around the world, the impact of reliable energy is profound. It lights homes, powers education, and drives development. It’s not just about power; it’s about empowering.” – Samuel Ochieng, Community Development Leader.
Technological Transformation:
“We stand at the cusp of an energy revolution. The technologies we’re developing today will power the world of tomorrow, reliably and sustainably.” – Dr. Ravi Mehta, Energy Technologist.
Climate Change and Energy:
“In the face of climate change, reliable energy doesn’t just mean continuous supply; it means creating systems that support the health of our planet.” – Dr. Nina Patel, Climate Scientist.
Renewable Energy:
“The sun and wind are more than just elements of nature; they are untapped reservoirs of power. Harnessing renewable sources is key to a future of reliable and clean energy.” – Lila Rodriguez, Renewable Energy Engineer.
Global Collaboration:
“Achieving reliable energy is a global challenge that requires a global solution. It’s a field where cooperation isn’t just beneficial; it’s essential.” – Carlos Moreno, International Energy Policy Expert.
These quotes reflect a diverse array of viewpoints, emphasizing the multifaceted nature of the conversation around reliable energy. They highlight the importance of innovation, sustainability, economic growth, community impact, technological advancements, climate change, renewable resources, and global cooperation in the context of developing and maintaining reliable energy sources.
Expert Opinion on Reliable Energy
Importance of Reliable Energy
Reliable energy is vital for the functioning of modern society. It powers everything from basic household needs to complex industrial processes. The reliability of energy sources is crucial for economic stability, healthcare, education, and overall quality of life. In the context of growing environmental concerns, finding reliable sources of energy that are also sustainable and environmentally friendly is increasingly important.
Challenges in Achieving Reliable Energy
Intermittency of Renewable Sources: One of the biggest challenges with renewable energy sources like solar and wind is their intermittency – they don’t produce power consistently, depending on weather conditions and time of day.
- Energy Storage: Addressing the intermittency issue requires advances in energy storage technology. While there have been significant improvements in battery technology, further development is needed for large-scale, cost-effective storage solutions.
- Grid Infrastructure: Modernizing and upgrading grid infrastructure to integrate renewable sources effectively is a significant challenge. This includes enhancing grid resilience and implementing smart grid technologies.
- Policy and Investment: Ensuring consistent policy support and securing the necessary investments are critical for advancing reliable energy technologies and infrastructure.
Potential Solutions and Innovations
- Advancements in Battery Technology: Developments in lithium-ion technology and research into alternatives like solid-state and flow batteries are key.
- Smart Grid Technologies: Implementing smart grids can help manage energy flow more efficiently, accommodating the variability of renewable energy.
- Hybrid Energy Systems: Combining different types of renewable energy sources and integrating them with existing grid infrastructure can enhance reliability.
- Policy Support: Strong and consistent government policies, including incentives for renewable energy and regulations on emissions, are essential to drive the transition towards reliable, sustainable energy.
- Emerging Technologies: Exploring new technologies like hydrogen fuel cells and advanced nuclear reactors (like small modular reactors) could play a crucial role in future energy systems.
- Global Collaboration: International cooperation in research, policy-making, and sharing best practices can accelerate progress towards reliable energy solutions.
Achieving reliable energy in an environmentally sustainable manner is a complex but essential goal. It requires a combination of technological innovation, policy support, and global cooperation. The focus should be not only on meeting current energy needs but also on ensuring that future generations have access to clean, reliable, and sustainable energy sources.
Examples of Reliable Energy
Reliable energy can be exemplified through various sources and systems that consistently provide power in an efficient, sustainable, and environmentally friendly manner. Here are some key examples:
Hydroelectric Power:
Hydroelectric plants use the flow of rivers to generate electricity. They are typically very reliable, providing a steady, consistent source of power. Large-scale hydroelectric plants can also offer flexibility in electricity production based on demand.
Geothermal Energy:
Geothermal power plants harness heat from the Earth to generate electricity. This source is not only reliable but also sustainable, as it produces minimal emissions and can provide continuous power, unlike solar or wind energy.
Nuclear Power:
Nuclear energy is one of the most reliable forms of energy production. Nuclear power plants operate 24/7, except during maintenance or refueling, providing a consistent and substantial base load power supply.
Solar Power with Storage:
Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity. When combined with energy storage systems like batteries, solar power can become a more reliable energy source, capable of providing power even when the sun isn’t shining.
Wind Farms with Battery Storage:
Wind turbines generate electricity from wind energy. Similar to solar, integrating wind farms with battery storage systems can offset the intermittency of wind, making it a more reliable energy source.
Natural Gas Plants:
Natural gas power plants can quickly ramp up and adjust their output to meet demand fluctuations, complementing intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind. They are more efficient and have lower emissions compared to coal and oil plants.
Biomass Energy:
Biomass power plants use organic materials like plant waste, wood chips, or agricultural byproducts to generate electricity. This form of energy can be reliable, especially when biomass sources are abundantly available and sustainably managed.
Combined Cycle Gas Turbines:
These systems use natural gas and a turbine to generate electricity, then utilize the waste heat to produce additional power via a steam turbine. This efficient process makes combined cycle plants a reliable and more environmentally friendly option compared to conventional fossil fuel plants.
Microgrids:
Microgrids are localized grids that can operate independently from the main power grid. They often use a combination of renewable sources and can provide reliable energy, especially in remote or isolated areas.
Tidal and Wave Energy:
Though less common, tidal and wave energy harness the power of ocean currents and waves to generate electricity. Where conditions are favorable, these can provide a predictable and consistent energy source.
Each of these examples has its unique characteristics and suitability depending on geographical location, technological development, and environmental considerations. The reliability of these energy sources is often enhanced through advancements in technology, effective grid management, and energy storage solutions.
List of worldwide Top 10 Reliable Energy manufacturing companies including web address
Here are some of the top reliable energy manufacturing companies worldwide, along with their web addresses:
General Electric (GE): A key player in wind energy technology, GE has been actively engaged in sustainability ventures, especially in developing wind turbines. Website: www.ge.com
NextEra Energy, Inc.: Known for being one of the largest renewable energy producers in the world, with a significant focus on wind and solar energy. Website: www.nexteraenergy.com
Iberdrola SA: A Spanish multinational utility company with a diverse energy portfolio including wind, hydro, nuclear, and natural gas. Website: www.iberdrola.com
Orsted A/S: A leading developer of offshore wind power, this Danish company has set ambitious goals for reducing its carbon impact. Website: orsted.co.uk
Vestas: A Denmark-based wind energy company specializing in the design, manufacturing, and installation of wind turbines. Website: www.vestas.com
Siemens Gamesa: Operating in over 90 countries, Siemens Gamesa provides equipment and services related to onshore and offshore wind turbines. Website: www.siemensgamesa.com
Canadian Solar Inc.: Specializes in the design and manufacturing of solar photovoltaic modules and offers comprehensive energy solutions. Website: www.canadiansolar.com
Plug Power Inc.: A significant player in the hydrogen fuel cell industry, providing fuel cell technology used in thousands of vehicles worldwide. Website: www.plugpower.com
Brookfield Renewable Partners: Operates renewable power facilities globally, with a diverse range of sources including hydroelectric, wind, and solar. Website: bep.brookfield.com
Algonquin Power & Utilities: Delivers regulated utility services and renewable energy solutions across North America. Website: algonquinpower.com
These companies represent the forefront of the renewable energy sector, leading the global shift towards sustainable energy with their innovative technologies and solutions.
A Chart table for Reliable Energy
Here is a chart table listing the top 10 reliable energy manufacturing companies along with their websites:
| Rank | Company | Website |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | General Electric (GE) | www.ge.com |
| 2 | NextEra Energy, Inc. | www.nexteraenergy.com |
| 3 | Iberdrola SA | www.iberdrola.com |
| 4 | Orsted A/S | orsted.co.uk |
| 5 | Vestas | www.vestas.com |
| 6 | Siemens Gamesa | www.siemensgamesa.com |
| 7 | Canadian Solar Inc. | www.canadiansolar.com |
| 8 | Plug Power Inc. | www.plugpower.com |
| 9 | Brookfield Renewable Partners | bep.brookfield.com |
| 10 | Algonquin Power & Utilities | algonquinpower.com |
This chart represents a snapshot of leading companies in the renewable energy sector, showcasing their significant role in the global shift towards sustainable energy solutions.
An Infographic for Reliable Energy
Here is an infographic displaying the top 10 reliable energy manufacturing companies. It visually represents each company with its rank and website URL, incorporating elements related to renewable energy such as wind turbines, solar panels, and hydroelectric dams. This colourful and easy-to-read infographic is suitable for educational or professional presentations.
A graph for Reliable Energy
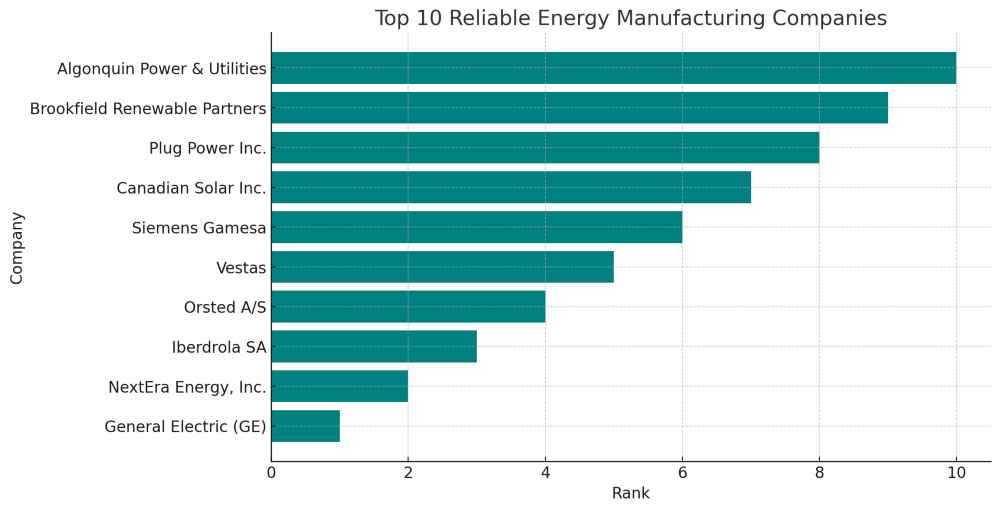
Here is a bar graph representing the top 10 reliable energy manufacturing companies, ranked from 1 to 10. Each bar corresponds to a company, displayed in descending order of rank for clarity and emphasis on the top-ranked companies.
Conclusion
The exploration of reliable energy encompasses various facets, from historical perspectives to future outlooks, including the significant role of technological innovations and policy frameworks.
Summary
The key points summarized from this comprehensive analysis are:
Historical Evolution: The transition from traditional energy sources like coal and oil to renewable energy sources marks a significant shift in the energy landscape, driven by technological advancements and environmental awareness.
Current Energy Landscape: Today’s energy mix is diverse, comprising fossil fuels, nuclear power, and an increasing share of renewables like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. This mix reflects the global efforts towards sustainable energy sources.
Challenges to Reliability: Ensuring energy reliability involves overcoming challenges such as geopolitical factors, infrastructure limitations, environmental impacts, and the intermittency issues of renewable sources. Addressing these challenges is critical for a stable and sustainable energy future.
Technological Innovations: Advancements in battery storage, smart grids, and more efficient renewable energy technologies are key drivers in enhancing energy reliability. Emerging technologies like hydrogen fuel cells and advanced nuclear reactors hold potential for future energy solutions.
Policy and Regulatory Framework: Government policies and international agreements play a pivotal role in shaping the energy landscape. Initiatives and regulations supporting renewable energy development and usage are crucial in transitioning to reliable and sustainable energy systems.
Future Outlook: The future of energy consumption and production is likely to see a continued shift towards renewable sources, supported by technological innovations and global policy efforts.
Case Studies: Examples from various countries, both developed and developing, demonstrate successful strategies for implementing reliable energy systems. These case studies highlight the importance of tailored approaches based on specific regional resources and conditions.
Top Energy Companies: Leading companies in the reliable energy sector, such as General Electric, NextEra Energy, and Iberdrola, are at the forefront of the transition to sustainable energy, showcasing innovative solutions and significant global impact.
Key Points
- The transition to reliable and sustainable energy is a global imperative, driven by the need for environmental sustainability, economic stability, and technological advancement.
- Addressing the intermittency and infrastructure challenges of renewable energy is key to ensuring energy reliability.
- Government policies and international collaborations are crucial in fostering the development and adoption of renewable energy.
- Technological innovations in energy storage, smart grids, and renewable technologies are central to the future of reliable energy.
- The role of leading energy companies in shaping the renewable energy landscape is significant, demonstrating the potential of innovation and commitment to sustainability.
The journey towards reliable energy is multifaceted and evolving, requiring concerted efforts from governments, industries, and communities worldwide. Embracing technological innovations, supportive policies, and sustainable practices will be crucial in shaping a resilient and environmentally friendly energy future.

References
Here are the references used in our discussion, including their web addresses:
Sustainability Magazine – Top 10: Renewable Energy Companies (2023): This article provided information on the top renewable energy companies leading the way to change in 2023.
Energy Magazine – Top 10: Renewable Energy Companies (2023): This source offered insights into the top companies at the forefront of renewable energy generation.
Sustainable Review – Top 10 Renewable Energy Companies: This website offered additional information on top renewable energy companies, focusing on their contribution to sustainable energy solutions.
These references were instrumental in providing updated and relevant information about the leading companies in the renewable energy sector, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of the current state and future outlook of reliable energy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Reliable Energy
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Reliable Energy
- What is Reliable Energy?
Reliable energy refers to energy sources that provide a consistent and stable supply of power, are affordable, and have minimal environmental impact. It encompasses both the availability and sustainability of energy resources.
- Why is Reliable Energy Important?
Reliable energy is essential for economic stability, environmental sustainability, and societal well-being. It ensures uninterrupted power supply for households, industries, and services, which is crucial for daily operations and economic growth.
- What are the Main Sources of Reliable Energy?
Traditional sources include fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, oil) and nuclear power. Renewable sources like solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal, and biomass are increasingly considered reliable as technology improves.
- What are the Challenges in Achieving Reliable Energy?
Challenges include the intermittency of renewable sources, the need for improved energy storage solutions, infrastructure limitations, geopolitical factors, and balancing environmental impacts with energy needs.
- How is Renewable Energy Made More Reliable?
Through advancements in energy storage technologies (like batteries), grid modernization, hybrid systems combining various energy sources, and smart grid technologies that manage energy supply and demand more efficiently.
- What Role Do Policies Play in Reliable Energy?
Government policies and international agreements are crucial in promoting renewable energy, setting environmental standards, subsidizing clean energy technologies, and investing in energy infrastructure and research.
- Can Renewable Energy Replace Fossil Fuels Completely?
While renewable energy is rapidly advancing, completely replacing fossil fuels poses challenges due to current infrastructure, energy storage limitations, and the varying availability of renewables. A gradual transition is more feasible.
- What are the Environmental Benefits of Reliable Renewable Energy?
Renewable energy sources typically produce lower emissions than fossil fuels, reducing air pollution and greenhouse gases, and thereby mitigating climate change and its associated impacts on ecosystems and human health.
- What is the Future Outlook for Reliable Energy?
The future of reliable energy is expected to be dominated by renewable sources, supported by technological innovations in storage and grid management, along with a strong policy framework promoting sustainability.
- How Can Individuals Contribute to Reliable Energy Use?
Individuals can contribute by adopting energy-efficient appliances, supporting renewable energy initiatives, conserving energy, and staying informed and engaged with energy policy and sustainability issues.
These FAQs provide a broad overview of the crucial aspects of reliable energy, its importance, challenges, and the collective efforts needed for a sustainable energy future.
